Paper manufacturing
Pulp Preparation
1 - Disintegration
The pulp is mixed with water to a consistency of approximately 8% fiber and 92% water. Additives are then added to define the opacity, brightness and color of the paper.
2 - Refining
To avoid build-up accumulation, refining separates fibers from each other, which are mixed and stirred in a large vat in order to obtain a completely uniform pulp.
3 - Screening and Treatment
The screening and treatment phase removes all debris and agglomerations from the pulp to improve fiber dispersion. |
 |
Paper Machine
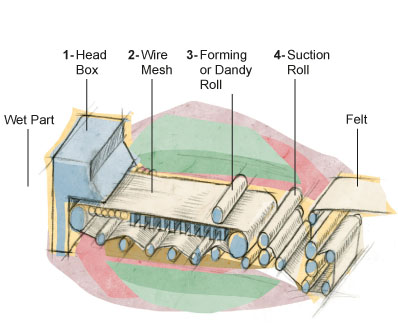
1 - Head Box
A contstant amount of pulp is pumped evenly, across the machine’s width, from the head box onto the wire.
2 - Wire
A woven mesh made from synthetic filaments, permits water drainage from the pulp through gravitational pull, thereby allowing the fibers to settle properly to form a wet sheet.
3 - Forming or Dandy Roll
A mesh covered roll that pierces air bubbles that may have formed and improves the sheet formation. The forming roll can be replaced by a dandy roll with a pattern used to make a watermark on the paper.
4 - Suction Roll and Felt
The paper passes through a suction roll in order to remove as much water as possible before arriving at felt section to start the drying stage. At that time, the sheet contains approximately 50 to 60% humidity/moisture. |
 |
Drying
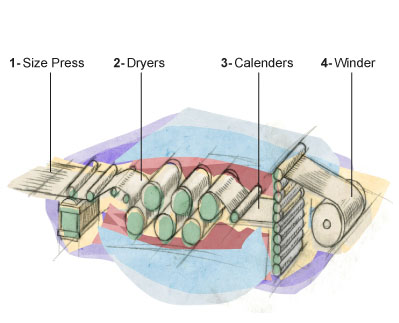
1 - Size Press
The size press applies a light film and continuous starch on both sides of the sheet. This treatment hardens the paper’s surface and fixes the fibers so that the sheet is able to resists penetration of liquid inks.
2 - Dryers
The paper passes through a series of steam-heated cylinders shaped like an accordion. The evaporation rate is constant and increases rapidly from one cylinder to another.
3 - Calenders
Calendering determines the finished of the paper. The sheet passes through two adjacent rollers which rotate to smooth and compress in the same way on both sides.
4 - Winder
The paper is wrapped on a wide metal mandrel to create a master roll, which is then transferred to a jumbo roll using a crane for the winding step. The master roll is held and then cut into strips according to the needed width, to then be finally wound onto cardboard cores. |
 |




